1.Magnesium's Role in Cannabis Plants:
Essential for Chlorophyll Production: Magnesium is a key component of chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for photosynthesis, which is how cannabis plants convert sunlight into energy.
Enzymatic Activity: Magnesium is involved in numerous enzymatic reactions, including those related to carbohydrate metabolism, protein synthesis, and energy production.
Nutrient Uptake: Magnesium helps regulate the uptake of other essential nutrients, such as phosphorus and potassium.
2.Causes of Magnesium Deficiency in Cannabis:
Soil pH: Magnesium availability is affected by soil pH. Low pH (acidic soil) can make magnesium less available to plants.
Soil Type: Sandy soils tend to have lower magnesium levels than clay soils.
Overwatering: Excessive watering can leach magnesium from the soil.
Nutrient Imbalances: High levels of other nutrients, like potassium, can inhibit magnesium uptake.
3.Optimal Magnesium Levels:
Soil Testing: The optimal magnesium level for cannabis plants varies depending on the soil type and growing conditions. Soil testing is crucial to determine the specific needs of your plants.
Typical Range: Generally, a magnesium level of 100-200 ppm (parts per million) in the soil is considered ideal for cannabis.
3.1.The Function of Magnesium in Cannabis Plants
Promote the formation of chlorophyll, which is essential to photosynthesis.
Support the transport and metabolism of other nutrient compounds, particularly phosphorus.
Promote the formation of vital plant proteins.
Support the synthesis of nucleic acid, a compound vital to the growth and differentiation of healthy plant cells.
Regulate the proper formation of stomata, which manage gas and water exchange between plants and their environment.
Regulate multiple plant enzymes.
4.Identifying Magnesium Deficiency and Toxicity:
4.1.Magnesium Deficiency
Visual Symptoms:
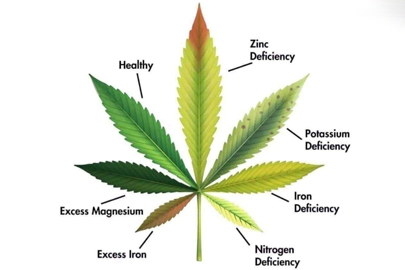
Chlorosis: The most common symptom is interveinal chlorosis, where the leaf tissue between the veins turns yellow, while the veins themselves remain green. This is often seen in older leaves first, as magnesium is mobile within the plant and can be redistributed to younger, growing tissues.
Necrosis: As the deficiency worsens, the yellowed areas may turn brown and necrotic (dead). This can start at the leaf tips and margins and progress inwards.
Leaf Curling: The leaves may curl upwards or downwards, depending on the severity.
Stunted Growth: The plant may exhibit stunted growth, with smaller leaves and reduced overall size.
Reduced Flowering: Deficiency can also impact flowering, leading to smaller, less dense buds.
Location: Magnesium deficiency often manifests in older leaves first, as the plant relocates magnesium from older tissues to newer growth.
Other Factors: The symptoms can be exacerbated by high levels of other nutrients, such as potassium, which can compete with magnesium for uptake.
4.2.Magnesium Toxicity
Rarity: Magnesium toxicity is relatively rare in cannabis plants, as it's not typically applied in high concentrations.
Symptoms: If excessive amounts of magnesium are present, it can disrupt the uptake of other essential nutrients, leading to nutrient imbalances and growth problems.
Visual Cues: Symptoms can include:
Leaf Curling: Similar to deficiency, but the curling may be more pronounced and may involve the entire leaf.
Stunted Growth: The plant may exhibit stunted growth and reduced vigor.
Nutrient Imbalance Symptoms: Other nutrient deficiencies may appear, such as calcium or potassium deficiencies.
4.3.Tips for Diagnosis:
Soil Testing: The most accurate way to determine magnesium levels is through a soil test. This will give you a quantitative measurement of the available magnesium in your growing medium.
Visual Inspection: Carefully observe your plants for the visual symptoms listed above, paying attention to the location and severity of the symptoms.
Compare to Healthy Plants: Compare your plants to healthy, thriving cannabis plants to get a better sense of what normal growth should look like.
5.Calcium's Importance in Cannabis:
Cell Wall Structure: Calcium is essential for the formation and strength of cell walls, which provide structural support to the plant.
Nutrient Transport: Calcium plays a role in the transport of nutrients within the plant.
Hormonal Regulation: Calcium is involved in the regulation of plant hormones, which control growth and development.
6.Can Marijuana Weed Be Nitrogen Deficient
Cannabis weed may indeed suffer from a nitrogen deficiency during growth. Nitrogen is one of the essential nutrients for plant growth and is mainly used to synthesize proteins and chlorophyll to promote plant growth and development. Symptoms of nitrogen deficiency usually include:
Yellowing of leaves: especially in older leaves, yellowing may occur first.
Slow growth: overall plant growth slows down, which may lead to a decrease in yield.
Smaller leaves: Newborn leaves may become smaller and the color of the leaves may not be as vibrant.
To avoid a nitrogen deficiency, you can apply a nitrogen-containing fertilizer regularly during cultivation to ensure that cannabis grass is getting enough nutrients. If you notice symptoms of a nitrogen deficiency, timely supplementation of nitrogen fertilizer will help restore healthy plant growth.
7.Deficiency Symptoms in Cannabis Flowers:
Bud Rot: Calcium deficiency can weaken cell walls, making buds more susceptible to rot.
Brittle Stems: Calcium deficiency can lead to weak stems that are prone to breaking.
Reduced Resin Production: Both calcium and magnesium deficiencies can reduce the production of trichomes, which contain cannabinoids and terpenes.
8.Addressing and Preventing Deficiencies:
Soil Amendments: Use magnesium sulfate (Epsom salts) or calcium sulfate (gypsum) to supplement soil with magnesium and calcium.
Foliar Feeding: Apply magnesium and calcium solutions directly to the leaves for faster absorption.
pH Adjustment: Adjust soil pH to the optimal range for magnesium and calcium availability.
Nutrient Balance: Ensure a balanced nutrient solution to prevent imbalances that can inhibit nutrient uptake.
9.Major Countries Where Cannabis Flower is Grown Include:
USA: California, Colorado and Oregon, in particular, are important growing regions due to their legalization policies.
Canada: since full legalization in 2018, Canada has become one of the largest legal cannabis markets in the world.
NETHERLANDS: While cannabis is not fully legalized in the Netherlands, its “coffee shop” culture has made it an important center for cultivation and consumption.
Uruguay: Uruguay was the first country in the world to fully legalize cannabis, boosting cannabis cultivation.
Israel: Israel is a leader in medical marijuana, driving cannabis research and cultivation.
Australia: The cultivation and use of medical cannabis has been legalized in certain states.